nuchal translucency thickness test|nuchal thickness chart : China NT screenings only show the risk of the fetus having a condition. If your screening is abnormal, your healthcare provider can use a test like chorionic villus sampling(CVS) or amniocentesis (later in pregnancy) to diagnose the condition. CVS is when tissue is taken from your placenta and tested for genetic conditions. . See more WEBA Churrascaria Estância é a maior e melhor escolha em Osasco e região. Somos mais do que uma churrascaria; somos um destino para a alma e os sentidos. Junte-se a nós e .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBTinker Bell is a 2008 American animated film and the first installment in the Disney Fairies franchise produced by DisneyToon Studios. It is about Tinker Bell, a fairy character created by J. M. Barrie in his 1904 play .
NT screenings only show the risk of the fetus having a condition. If your screening is abnormal, your healthcare provider can use a test like chorionic villus sampling(CVS) or amniocentesis (later in pregnancy) to diagnose the condition. CVS is when tissue is taken from your placenta and tested for genetic conditions. . See more
The amount of fluid in your fetus's neck increases with gestational age. Different organizations have slightly different cutoffs at which they’ll recommend . See moreNo, an abnormal nuchal translucency scan doesn’t mean the fetus has Down syndrome or any other congenital syndrome. It might mean the fetus is at a higher . See more
Most healthcare providers can interpret the NT ultrasound on the same day. Blood work collected from the first-trimester screening will take at least a few days . See more
An increased nuchal translucency increases the probability that the fetus will be affected by a chromosomal abnormality, congenital cardiac defects, or intrauterine fetal demise. Typically, nuchal translucency alone is not sufficient as a screening test for chromosomal abnormalities. How to define a normal or abnormal nuchal translucency measurement can be difficult. The use of a single millimeter cutoff (such as 2.5 or 3.0 mm) is inappropriate because nuchal translucency . A nuchal translucency screening, or NT screening, is a specialized routine ultrasound performed at the end of the first trimester of pregnancy. It helps doctors determine if a baby is statistically more likely to have a chromosomal .This leaflet is to help you understand what Nuchal Translucency (NT) is, what tests you need, and the implication of being diagnosed for you, your baby, and your family.
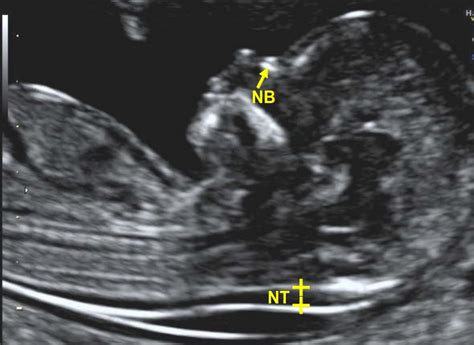
Purpose. NTs are conducted to assess the nuchal folds on the back of the fetus’s neck. By measuring the thickness of the nuchal folds—an indicator of how much fluid there is inside the folds—the risk of possible issues .The nuchal translucency test measures the nuchal fold thickness. This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down . The nuchal translucency test (also called the NT scan) uses ultrasound to assess your developing baby's risk of having Down syndrome (DS) and some other chromosomal .
The nuchal translucency test measures the nuchal fold thickness. This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down .The nuchal translucency test measures the nuchal fold thickness. This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down . The nuchal (say "NEW-kuhl") translucency screening is a test done during pregnancy. It uses ultrasound to measure the thickness of the fluid buildup at the back of the .The nuchal translucency test measures the nuchal fold thickness. This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down syndrome and other genetic problems in the baby.
This is available to pregnant people from weeks 11 through 13 of pregnancy. It comprises a maternal blood test and a nuchal translucency test, which is ultrasound imaging of the fetus to look for clues that could affect the chances .NIPT has a false-positive rate of 0.1 per cent, which means it gives fewer false-positive results than the combined test. What is a normal nuchal translucency measurement? An NT of less than 3.5mm is considered normal when your .
nuchal translucency ultrasound images
Normal thickness: All fetuses develop a measurable nuchal translucency at some point in the first trimester. Thickness of the translucency varies with gestational age: Peak thickness at 12-13 weeks (in 75% of fetuses). At 12-13 weeks the 50th percentile thickness = 1.7mm. At 12-13 weeks the 95th percentile thicknessThe nuchal (say "NEW-kuhl") translucency screening is a test done during pregnancy. It uses ultrasound to measure the thickness of the fluid buildup at the back of the developing baby's neck. If this area is thicker than normal, it can be an early sign of Down syndrome , trisomy 18 , or heart problems. Nuchal translucency (NT) is a measure of a thickness of a fold located on the fetuses' neck. This fold's greater thickness is connected to the greater prevalence of genetic disorders, fetal death, and its major abnormalities.NT is one of the 1st trimester screening methods.. We perform a nuchal translucency test during the ultrasound examination in the .Nuchal translucency (NT) is the sonographic appearance of a collection of fluid under the skin behind the fetal neck in the first-trimester of pregnancy. . In fetuses with chromosomal abnormalities, cardiac defects and many genetic syndromes the NT thickness is increased. Screening by NT can detect about 80% of fetuses with trisomy 21 and .
glycol refractometer with case
Radiopaedia.org, the peer-reviewed collaborative radiology resource A sample of the mother's blood, an evaluation of the baby's nasal bone and a consultation of the nuchal translucency thickness all combine to let the parents know their child's chances of having Down syndrome. . However, with the combined test, the false positive rate is still five percent. Therefore, the nuchal translucency normal range .
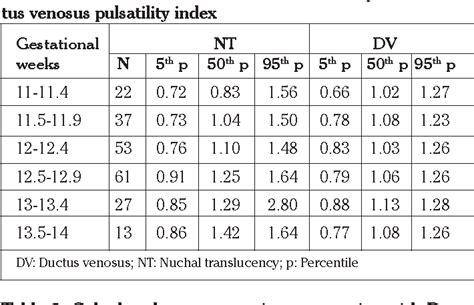
Fetal nuchal translucency (NT) thickness is the single most effective marker of trisomy 21 and all other major chromosomal defects. It increases with crown–rump length (CRL), and it is important to take gestational age into account when determining whether a given NT thickness is increased 1 .
glycol viscosity refractometer
nuchal translucency normal range chart
A nuchal translucency scan is an ultrasound scan that measures the thickness of the space behind your baby’s neck. . If you are having the combined first trimester screening, you will also need a blood test. Can a nuchal translucency scan harm my baby? Ultrasounds do not harm you or your baby or increase your risk of miscarriage.The nuchal translucency test measures the nuchal fold thickness. This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down syndrome and other genetic problems in the baby.Home > Calculators > Crown Rump Length and Nuchal Translucency Enter the CRL and press calculate to obtain the estimated gestational age and expected nuchal translucency thickness. The calculator will also give the percentile for a measured NT if entered for CRL 40 to 85 mm.

The first-trimester screening also known as nuchal translucency screening, or NT, is a prenatal test, ultrasound and a blood test that can help determine the likelihood of having Down Syndrome. . The transvaginal ultrasound component, known as nuchal translucency (NT) screening, measures the thickness of the space at the back of the fetus’s .
The nuchal (say "NEW-kuhl") translucency screening is a test done during pregnancy. It uses ultrasound to measure the thickness of the fluid buildup at the back of the developing baby's neck. If this area is thicker than normal, it can be an early sign of Down syndrome , trisomy 18 , or heart problems. NUCHAL CORD AND ITS CLINICAL EFFECTS ‘Nuchal cord’ refers to umbilical cord encircling the fetal neck. Nuchal cord can have clinical implications on NT and nuchal fold thickness (NFT) measurements, in the first and second trimesters of the pregnancy, respectively [].Nuchal cord can cause indentation of the fetal skin, thus causing displacement of the fluid in . The risk for chromosomal aberrations in fetuses with nuchal translucency 3.0‐3.4 mm is 1:7.4, the risk after normal NIPT for common trisomies is 1:21, therefore offering an invasive test with chromosomal microarray could be considered.
Nuchal translucency (NT) is the sonographic appearance of a collection of fluid under the skin behind the fetal neck in the first-trimester of pregnancy. . In fetuses with chromosomal abnormalities, cardiac defects and many genetic syndromes the NT thickness is increased. Screening by NT can detect about 80% of fetuses with trisomy 21 and .
Objective: Fetal nuchal translucency (NT) thickness increases with crown-rump length (CRL). In screening for chromosomal defects patient-specific risks are derived by multiplying the a priori maternal age-related risk by a likelihood ratio, determined from the deviation of the measured NT from the expected median.Nuchal translucency (NT) screening is a prenatal test that assesses the thickness of the clear space at the back of a developing baby's neck during the first trimester of pregnancy. This non-invasive procedure provides valuable information about the baby's risk for certain chromosomal abnormalities and other potential health issues.
The nuchal translucency test measures the nuchal fold thickness. This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down syndrome and other genetic problems in the baby. . The nuchal translucency test is a screening test. It does not screen for genetic problems in babies.Normal thickness: All fetuses develop a measurable nuchal translucency at some point in the first trimester. Thickness of the translucency varies with gestational age: Peak thickness at 12-13 weeks (in 75% of fetuses). At 12-13 weeks the 50th percentile thickness = 1.7mm. At 12-13 weeks the 95th percentile thicknessWhat is a nuchal translucency scan? A nuchal translucency scan (also called an NT or nuchal scan) uses ultrasound to assess your baby’s risk of having Down syndrome and some other chromosomal abnormalities, as well as major congenital heart problems. You may be offered a nuchal scan as part of your prenatal screening (Audibert et al 2017, Chitayat et al 2017, .Nuchal Translucency (NT) scan: You will have an NT scan when you are between 11+2 weeks and 14+1 weeks pregnant. This measures the thickness of the fluid at the back of your baby’s neck. This measures the thickness of the fluid at the back of your baby’s neck.
nuchal translucency measurement chart
At times, the nuchal translucency test may add on ultrasound markers, such as measuring a baby's nasal bone. The combined result of the blood tests and the ultrasound gives you a sense of your . Nuchal translucency screening involves having an ultrasound of your abdomen in the first trimester of pregnancy. During the ultrasound, the healthcare provider measures the thickness of the tissue at the back of the fetus’ neck. This tissue is called the nuchal translucency. Thicker-than-normal nuchal translucency means that the baby has a .
Nuchal translucency thickness... 21 Womens’ attitudes to 1st versus 2nd trimester screening . . . 42 2. Sonographic features of chromosomal defects . screening for trisomy 21; for an invasive testing rate of 5%, about 75% of trisomic pregnancies can be .
15 de jun. de 2017 · 6 beds, 4 baths, 3976 sq. ft. house located at 1926 Pinnacle Ln, Prescott, AZ 86301 sold for $870,000 on Mar 4, 2022. MLS# 1044353. GORGEOUS 2 STORY HOME IN PINNACLE ESTATES * 6 BEDROOMS * 4 BA.
nuchal translucency thickness test|nuchal thickness chart